Which Light Bulbs Are Dimmable And Which Ones Aren’t?
If you are ever in the process of replacing a bulb on a dimmer circuit you may be wondering which bulbs are suitable to replace it with since not all bulbs can be dimmed.
While most light bulbs can be dimmed under the correct conditions there are instances where bulbs simply aren’t meant to be dimmed.
All incandescent and halogen bulbs can be dimmed on any dimmer since their construction is based on an electrically resistant tungsten filament. LEDs and CFLs bulbs are not always dimmable since they are electronic loads and aren’t compatible with a lot of common dimmers.
While this is the general answer to which bulbs can be dimmed it doesn’t give you a very comprehensive idea of why this is.
In this following article, we will go through all these bulbs individually and explain what makes them dimmable or not dimmable in more depth.
Are Incandescent Bulbs Dimmable?
Being the oldest and formerly the most popular type of bulb it makes sense to start by discussing the incandescent bulb.
All incandescent bulbs are dimmable with an effective dimming range of 0-100% of their total light output. This is because incandescent bulbs produce light through a tungsten filament which glows and “incandesces” once it reaches a high enough temperature.
Tungsten is a very robust and durable material, which makes it a suitable pick for a bulb like this since the temperature the filament reaches can be quite high. Click here for our article on Why Tungsten Is Used In Light Bulbs.
As mentioned, incandescent bulbs are able to be dimmed from 0-100% with practically any common dimming method. The dimming for the incandescent bulb is linear, meaning that if you decrease the power input by 20% the light level will also drop by that much.
This is different from bulbs based on electronic components and not pure electrically resistive loads due to how electronic components react quite differently to a decrease in power input.
Are LED Bulbs Dimmable?
When it comes to LED bulbs it really depends if they are dimmable or not, because some of them are and some of them are not.
In general, it is possible to dim LEDs like any other light bulb. They have an effective dimming range of 20-100% of their total light output. LEDs are also able to go to 0-20% but it is normally avoided since it ends up being less energy efficient at low percentages.
That said, LEDs are also an electronic load unlike incandescent bulbs, which means they require some specific conditions in order for proper dimming to take place.
Not all LEDs are designed to be dimmed. The difference between dimmable and non-dimmable LEDs lies within the driver that provides them with electricity.
The non-dimmable LED drivers are made to simply output an ON or OFF signal for its electrical current whereas a driver made for dimming is able to produce states of light between ON/OFF, such as 25/50/75%.
We have an entire article dedicated to If LEDs Bulbs Are Dimmable, which we recommend you go to if you want a more in-depth explanation than what is provided in this article.
As for the dimmable LEDs, they are normally dimmed in one of the two following ways:
- Phase Dimming (Pulse Width Modulation, PWM)
- Amplitude Width Modulation (AWM)
These dimming methods function quite differently. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) works by modifying the length of the sinewave which provides the LED with power.
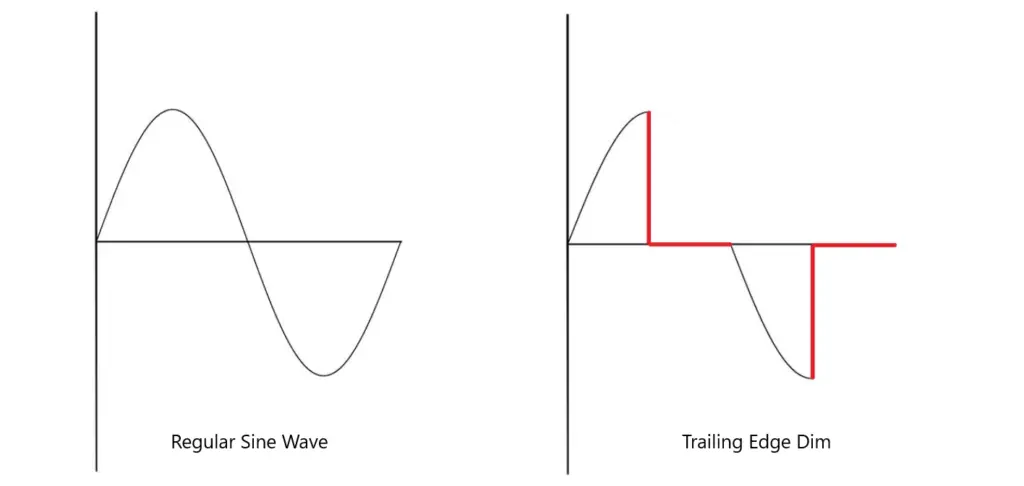
As you may be aware, LED lights do not continuously produce light when turned on. Without a high-frequency LED driver to bring up the frequency (Hertz, Hz) of the LED they normally turn on and off about 50-60 times per second. This is the equivalent of saying they run at 50-60 Hz.
By cutting off the sinewave you effectively cut off the amount of time the light gets turned on in its cycle.
The issue with this method is that it is liable to cause flickering since the shorter the sinewave is the more likely it is that we notice the lack of full cycles.
In order to compensate for this the LED is usually powered by a high-frequency driver, which usually bumps the frequency of the electricity to about 240Hz or higher.
The other method of dimming LEDs is Amplitude Width Modulation (AWM). This is conceptually much simpler than PWM since all you do for AWM is bring the electrical current down to dim the LED.
This works in a linear manner, meaning that if we have an LED that runs on 100mA at full power it will produce 80% of its max output at 80mA. This method works great but can however be inconsistent at power levels below 10-20%.
Are CFL Bulbs Dimmable?
CFL bulbs are a bit different from other bulbs on this list since they don’t behave the same as the others at all in terms of dimming them.
However, much like the LED, there are versions of CFL that are and are not dimmable. That said, in general, CFL bulbs are not dimmable nor should they try to be dimmed unless it is specified that they are dimmable.
The CFL technology normally works by charging up electrodes which discharge into the bulb. This discharge requires a buildup of energy and this buildup is much more complicated to achieve when subject to a dimmer circuit.
When a non-dimmable CFL is dimmed by non-compatible dimmers a few different problems can occur. Some of them include the following:
- Unpredicted flashing
- Flickering
- Decrease in bulb lifetime
As for the dimmable CFLs, they have an effective dimming range of around 30-100%. The reason they normally don’t go much lower than 30% is because at that level the light tends to become unstable and will in some cases fully turn itself off when attempted to be dimmed lower than this.
With all of this stated, it is generally wise to not dim a CFL unless it specifically says it can be dimmed as it probably will not work as well as you might expect it to. For more information regarding dimming CFLs, we recommend you go here.
Are Halogen Bulbs Dimmable?
Halogen bulbs are dimmable in the same way as incandescent bulbs are, which is because they are based on the same technology.
Halogen bulbs are fully dimmable with an effective dimming range of 0-100%. Much like incandescent bulbs, they produce light linearly in relation to the electrical current they receive.
Much like incandescent bulbs halogen bulbs produce light using a tungsten filament which gets heated up to extreme temperatures. Halogen bulbs excel at this due since they are able to run hotter than their incandescent counterpart due to the addition of halogen gas.
Considering its similarities to the incandescent bulb it makes sense that they would be dimmed in a similar fashion.
Summary
To summarize, here are the general dimmer compatibilities for the bulbs mentioned.
- Incandescent bulbs are compatible with practically all common dimmers and will dim between 0-100%
- LED bulbs come in different varieties and are not always dimmable. Some LEDs are equipped with drivers that only allow them to be turned on/off and nothing in between. As for dimmable LEDs, they have an effective dimming range of 20-100%.
- Halogen bulbs are compatible with most common dimmers and have an effective dimming range between 0-100%
- CFL bulbs are generally speaking not dimmable. While there are dimmable models of CFL bulbs they are far less common than the non-dimmable CFLs. If a CFL is dimmable it will most likely be advertised somewhere on its packaging.





