Do LED Strips Use A Lot Of Electricity?
When it comes to all of the modern-day lighting solutions LEDs are often brought up as one of, if not the best, options for home lighting. One application of LEDs that has been gaining a lot of traction in recent years is LED strips since they are much more versatile than any other light source currently available.
Seeing as how popular these lights are getting in recent years it has become common to wonder if these lights use a lot of electricity in comparison to other lighting solutions and how expensive they can be to run in terms of electricity costs.
LED strip lights are generally very cheap to operate and use very little electricity. Compared to incandescent bulbs they use about 90% less energy and about 70% less than halogen bulbs to produce the same amount of light. This is because LEDs have high efficiency and waste very little energy as thermal radiation.

How Much Power Do LED Strips Use?
The amount of power LED strips use can depend on the strength of the individual LED chips but also how long the strip is and how densely they are placed along the strip. This is simply due to the fact that the LED density and the length of the strip directly dictate how many individual LED chips need to be powered and therefore how much power will be used.
LED Density
As mentioned the LED density is important to power usage due to the increased amount of individual light-producing chips on the strip. There are three common LED densities for lighting strips, which are:
30 LEDs per meter (9 per foot)
60 LEDs per meter (18 per foot)
120 LEDs per meter (36 per foot)
While this is important for knowing the power usage it can also be important for the quality of light. Depending on the application and how far these strips are supposed to project their light there is a chance that the light will appear uneven if the density is too low.
It is also worth noting that the higher-density strips will cost a significant amount more due to the light-producing chips being the most expensive component in the entire strip.
LED Strip Power Usage
Now that we know how the density of LEDs affect power usage we can start charting the strip’s power usage with the parameters of its length and density.
This is however rather difficult to do since the power usage can vary a lot due to the different available models and those different LEDs will have different strengths. However, we can make a chart with an assumption of an individual LED chip strength of about 0,15W, which is on the higher end of energy usage and therefore brightness.
| @0,15W/LED Chip | 30 LED/m | 60 LED/m | 120 LED/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 Meters (~16,5 feet) | 22,5W | 45W | 90W |
| 10 Meters (~33 feet) | 45W | 90W | 180W |
| 15 Meters (~49 feet) | 67,5W | 135W | 270W |
| 20 Meters (~65,5 feet) | 90W | 180W | 360W |
| Watt per meter (W/m) | 4,5 W/m | 9 W/m | 18 W/m |
This shows us that there is a direct correlation between the amount of LEDs present and their power usage. These numbers are also on the higher end of the spectrum since it’s rare to use LED strips over 5 or 10 meters. Therefore it is safe to say that the LED specifications listed here are better suited for uses that require extra brightness or simply a large scale.
For something better suited for the home you probably don’t need something as strong as 0,15W/chip strips nor strips this long. A chart better suited for home lighting decor might look a bit more like this:
| @0,06W/LED Chip | 30 LED/m | 60 LED/m | 120 LED/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0,1 Meter (~4 inches) | 0,25W | 0,5W | 1W |
| 0,5 Meters (~1,5 feet) | 0,9W | 1,8W | 3,6W |
| 1 Meter (~3 feet) | 1,8W | 3,6W | 7,2W |
| 5 Meters (~16,5 feet) | 9W | 18W | 36W |
| Watt per meter (W/m) | 1,8 W/m | 3,6 W/m | 7,2 W/m |
While numbers may vary due to different factors such as LED quality and surrounding temperatures this is an accurate representation of how the electricity usage might look like for a standard LED strip made for home decor.
It is also worth noting that at lengths of 1 meter (~3 feet) and below the power usage will be slightly higher in proportion to the number of LEDs present since the driver will consume a larger portion of the power in comparison to the LEDs if the strip is shorter.

Comparing Power Usage With Other Bulbs
Now that we know roughly how much power LED strips use we can start comparing them to other available bulbs. For this comparison, we will use 1 meter of a 60 LED/m strip @0,06W. This is because this is projected to produce about 500 lumens evenly across the strip, which is the number we will use to keep the comparison even since lumen is just a quantified light output. This comparison would look like this:
| Incandescent | Halogen | CFL | LED Strip | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 Lumen | 40W | 31W | 10W | 3.6W |
What this shows us is that in comparison to most older traditional lighting methods LED strips are extremely efficient. They are 90% more efficient than incandescent, 85% more than halogens and 70% more than CFLs.
However, despite LED strips being far more efficient, it is not always wise to switch out existing lighting to only strips. LED strips’ main use is for decorations and accent lighting and is not meant to replace the common lighting in the room on its own. If you are looking for a replacement for the light bulbs you are better off looking at LED bulbs instead of strips.
Why LED Strips Use A Lot Less Energy Than Other Lights
As shown in the table above it is clear that LED strips are way more efficient than other light sources, but why is this? Simply put it is because LED technology is far better at not wasting inputted energy as thermal radiation, or in other words, heat.
Older bulbs such as incandescent and halogen emit light through a glow via a tungsten filament. This is accomplished by providing the filament with enough power for it to start glowing, which is much more than that of LED strips.
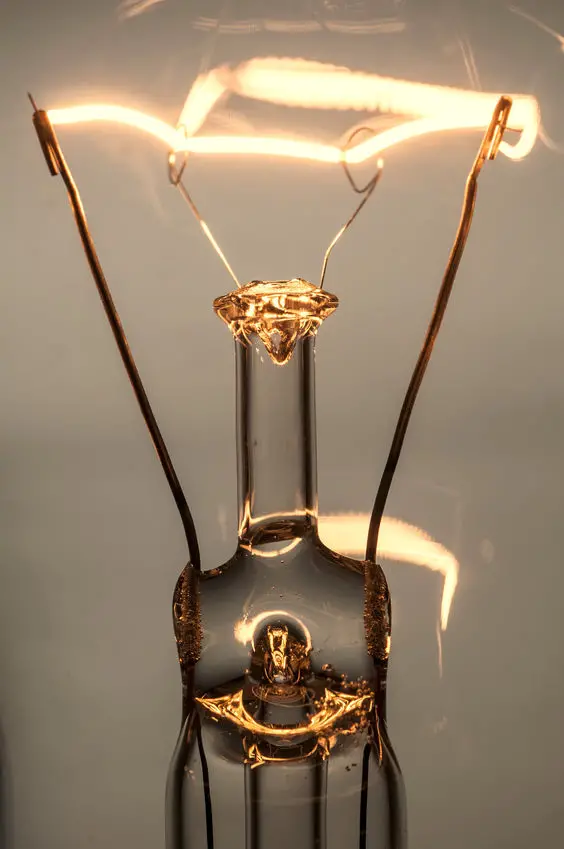

An incandescent bulb runs at a temperature of around 2500 °C (4600 °F) inside the filament whereas the individual LED chips generally run at anywhere around 20-80 °C (68-140°F) depending on how good its heat management is.
Heat management is also an aspect of LED strips that stand out. Since the heat build-up is dispersed throughout the entire strip there is no single point at which excessive heat builds up, contrary to an incandescent bulb.
This means that the LED strip theoretically is also more efficient than LED-based bulbs, since bulbs are often enclosed and not spread out as much as strips, however, they also have more advanced cooling methods such as heatsinks.
Operating Cost Of LED Strips
As we now have all the necessary knowledge and numbers of LED strips we can begin to look at how much it actually costs to operate these. Firstly we will begin to look at how much they cost in comparison to other types of bulbs.
For this comparison, we will use the exact same parameters for the LED strips as before, 1 meter of a 60 LED/m strip @0,06W per chip. When put up against the other bulbs it looks like this:
| @500 Lumen | CFL | Halogen | Incandescent | LED Strip |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light bulb projected lifespan | 10 000 hours | 5000 hours | 1000 hours | 50 000 hours |
| Watts per bulb/unit (the equivalent to 500 lumen) | 10W | 31W | 40W | 3,6W |
| Cost per bulb/unit | $5 | $2 | $1 | $15 |
| Kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity used over 50,000 hours | ~500 kWh | ~1550 kWh | ~2000 kWh | ~180 kWh |
| Cost of electricity (@ 0.10 per KWh) | $50 | $155 | $200 | $18 |
| Bulbs needed for 50 000 hours of use | 5 | 10 | 50 | 1 |
| Total cost for 50 000 hours | $75 | $175 | $250 | $33 |
When put head to head with the other bulbs it is clear to see that the LED strips have a clear advantage in that they are far more efficient even when outputting the same amount of light.
It is also worth noting that this chart assumes that you only use 1 meter out of the strip, which contributes to the wattage being so low. However, most strips are usually sold as 5 meters, meaning you can get more value out of your purchase by simply using more of the strip and not only 1 meter of it as we did in this comparison.
Conclusion
The main takeaway from this is that LED strips do not use a lot of electricity at all in comparison to most other lighting solutions. However, it can change drastically depending on how much of it you use and under what conditions these strips are put.
Since they are mainly meant to be used as accent and decoration lighting it is safe to say that they fill that role great since their low energy usage justifies it not having a directly productive purpose.