The Advantages Of LED Lighting
When speaking of modern lighting solutions LEDs are very often brought up as one of the best solutions for almost all applications. But why is this? Here we are going to attempt to answer that by listing some of the top advantages of LED lighting and explaining what makes these traits of LEDs so desirable.

Contents
High Energy Efficiency
One aspect of LEDs that make them so desirable is their general energy efficiency is very high. When measuring lighting in its efficiency the unit Lumen/Watt (lm/W) is commonly used. This number describes the amount of light (lumen) the light bulb gives off divided by the inputted energy (Watt), which gives an indicator as to how energy efficient the light is. This number is also commonly known as luminous efficacy.
Luminous efficacy is something that LEDs excel in when compared to other bulbs. LEDs are up to 90% more efficient than incandescent bulbs, 80% more than halogens and 60% more than CFLs.
The most common LEDs of today have a luminous efficacy of at least 150 lm/W and up to 200-220 lm/W, which is significantly higher than the 10-12 lm/W of the incandescent bulb and the 20-36 lm/W of halogen bulbs.
What this essentially means is that we can use a 7W LED to create an equal amount of light as a 40W incandescent bulb or a 30W halogen bulb, which is why LEDs are great to use since they use far less energy for equal results.
There are some bulb types that come close to it, such as fluorescent tubes and sodium-based lamps, however, they fail in a lot of other aspects where the LED does well.
Little Heat Emissions
The main reason why LEDs are more efficient than other bulbs is that their heat emissions are very low in comparison to the other bulbs.
An LED will have a temperature between 20-80 °C (68-140°F) in the junction, which is the place in which the light is created. In comparison, an incandescent bulb reaches temperatures of up to 2500 °C (4600 °F) in the tungsten filament where its light is created.
This has to do with how both of these lights produce light, to begin with. LEDs make use of something known as electroluminescence, which is most easily explained as a phenomenon of a material emitting light when an electric current or an electric field passes through it. This is a lot different to the way incandescent bulbs, which use an electric current to create an excessive heat generation that causes the filament in it to glow and emit light.
Almost all sources of light produce some sort of heat, it is simply a question about efficiency when looking at how much heat they generate. For a further comparison on heat emissions among different light bulbs, we recommend you go to our article on it here.
Little To No UV Emissions
Another advantage of LEDs is the fact that their UV emissions are very minimal if not nonexistent. The actual LED may create UV rays whilst creating its light, however, a very small amount of that UV actually gets emitted. This is because on top of every LED chip there is a layer of phosphor, which helps with the general quality of light.
What this phosphor layer does is that “slows down“ the created light and radiation a tiny bit, which is enough to cause the small amount of UV generated to turn into white light.
So while LEDs do create UV rays by the principle of electroluminescence it is such a small amount that gets emitted that it’s usually not even considered. Most older bulbs like incandescent and halogen also create a small amount of UV but all of the bulbs mentioned here don’t create enough UV to cause any damage to people or items.
LEDs Long lifespan
One field that LEDs dominate over other lighting solutions is their lifespan. LEDs will last somewhere between 50 000 and 100 000 hours depending on their construction, quality and heat management, which is roughly equivalent to 5,5-11 years of continuous light production.
If you were to compare LEDs to other light sources it quickly becomes apparent that LEDs have a very noticeable edge. There are a few reasons for this. The main reason for this is something we have already mentioned, that their heat generation is very minimal.
Heat and heat management are a very large part of how long a bulb will last, simply because high heat will degrade the bulb and cause it to last shorter than intended.
A chart comparing the different bulbs in their lifespan would look something like this;
Low Operating Cost
Another advantage of LEDs is that their operating cost is rather low. If we were to keep an average 11W, 800 Lumen LED on constantly it would cost approximately $19 per year in pure electricity cost. Having an equivalent incandescent bulb of 800 Lumen and 60W and cost around $83 per year under those same conditions.
This all has to do with the fact that LEDs use far less power (Watt) for the same results in comparison to other bulbs, which we’ve previously mentioned under the header “high energy efficiency“ as well.
Versatility Of LEDs
One more great thing about LEDs is that they are very versatile in how they can be used. LEDs are used in a plethora of different ways, such as in bulbs, in strips, in their own fixtures or even in electronical applications such as coloured light indicators.

This is because LEDs are very small and can be slotted in into almost any application. A lot of standard LEDs are only a few millimetres wide and come in a lot of different colours, which makes them great for a wide variety of uses.
They are also commonly used as chips, which are also usually only a few millimetres wide generally. These chips are however a lot more complicated than singular LEDs, as these chips will have several small LEDs in them to produce light. This is also how RGB features are created in LEDs, they are made by putting red, green and blue (RGB) LEDs into a chip and then sending the chip directional signals to tell it what colour to emit.
Increased Reliability
Another aspect of LEDs that is great is their increased safety in terms of how reliable they are. LEDs can function in a variety of different environments with many different temperatures without suffering too much as a consequence.
When pushed to its limits it will of course limit it in terms of lifespan, but when installed into less than ideal environments they can still persevere and last a respectable amount of time with little to no issues.
Instant Illumination
Unlike lights such as the CFL, the LED require very little time to reach its full light output from the moment it’s turned on. This is a very desirable trait of a light bulb for the home environment as it can be quite frustrating for the user to have to wait several minutes in order to have a decently illuminated home.
The reason why the LED requires only fractions of a second is that they start producing light the very moment an electrical current passes through it, which will happen the same instance its light switch is flicked.
This is very different from CFLs, which need a few minutes to build up enough electrical charge to kick themselves into its normal light output.
Directional Light
Another great part about LEDs is the fact that their light output is very directional. The LED chips which produce light are flat, meaning that they will only give off light towards one single direction in 180 degrees.
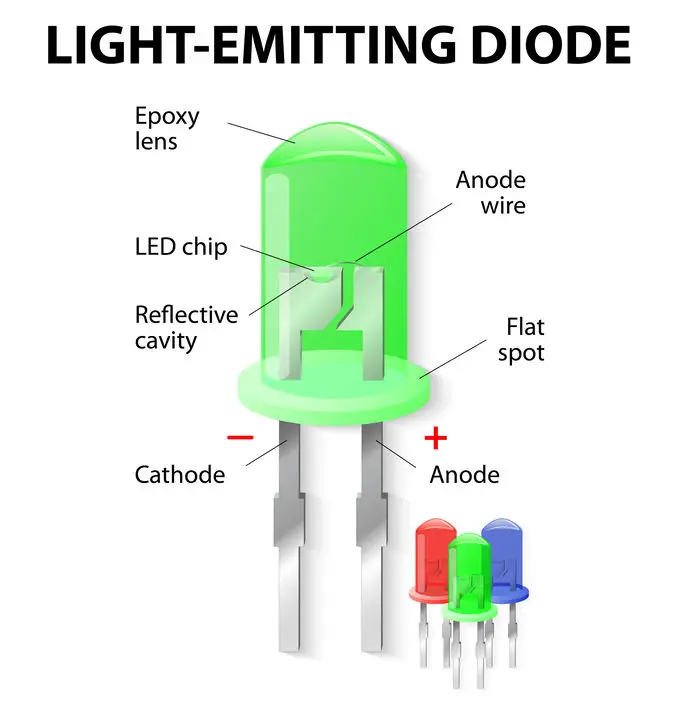
The reason this is a particularly good characteristic is simply that we get more control of where outputted light goes and do not waste the light on unwanted spots.
This can be compared to how an incandescent bulb will project light in every single direction, which in turn will mean that it projects less light than where it was originally intended to be projected.
This can however be seen as a negative if you wanted to have an omnidirectional light source with the purpose of lighting up the environment around it in its entirety.
However, this can be circumvented by making use of a retrofit LED bulb. These are light bulbs that look almost identical to old incandescent bulbs but use LED technology to produce light.
Wide Range Of Colour Temperature
One more great thing about LEDs is that they come in a very wide variety of colour temperatures (CCT/K). LEDs generally come in temperatures around 3000K or 4000K but can be produced to emit light anywhere between 2200K-20000K.
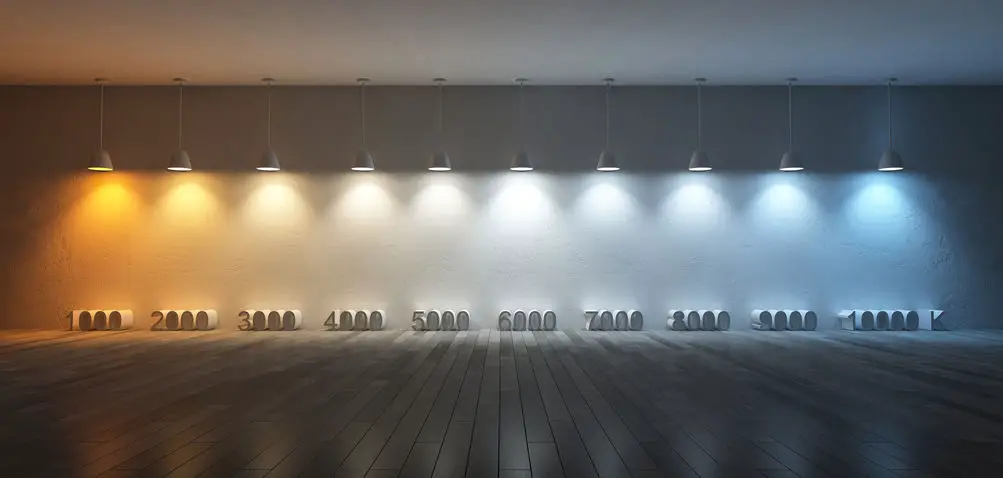

This can matter a lot because the colour temperature of light can impact the mood of a room a lot. This is why your home’s lighting will feel warmer and more inviting than that of the sterile lighting in hospitals, the colour temperature of your home is much warmer than hospital lighting.
The wide range of colour temperatures is achieved in two different ways. When making the LED warmer they simply apply additional phosphor on top of the existing LED. This has the effect of making the light more yellow/orange due to it changing the wavelengths of the normally emitted blue light rays into warmer colours.
When making cooler LEDs they simply make the LED chips contain a larger portion of blue LEDs and therefore making it give off a much cooler colour.
Good Colour Rendering (CRI)
In relation to colour temperature, LEDs also generally have good colour rendering. Colour rendering is simply a measurement of how well a light source will reflect light off an object to its original colour.

CRI is measured from 0 to 100 where 100 means a perfect colour rendering and 0 means that it gives off colour right in 0% of the colour spectrum. Normally speaking anything that is CRI rated as 80 or above is considered good and 90+ is considered very good.
The CRI of LEDs can vary quite a lot depending on the quality of it, however, it is usually rated between 80-90. This is because in most scenarios a CRI of 80-90 will be just fine, since anything above that is usually only needed if the light is supposed to illuminate something highly colourful or important, such as makeup mirrors or in an art gallery.
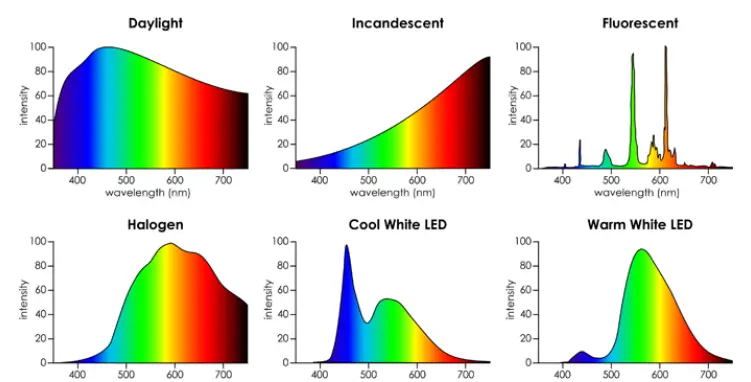
Even in these scenarios, however, the LED can still be viable since there are versions of it that can rate up to CRI 99, or otherwise known as “full-spectrum LEDs“.
The reason why it won’t be rated CRI 100 is that CRI is a measurement that is based on the spectral distribution of the sun and the LED simply can’t balance the reds and blues perfectly using today’s solutions. It is however speculated that CRI 100 LEDs will be available in the market soon enough.
LEDs Are More Sustainable
The last thing we want to mention about the advantages of LEDs is that they are safer for the environment in terms of the materials used to create them.
Unlike the mercury bulb, CFLs and fluorescent tube lights there are no traces of mercury inside of LEDs, which makes them a lot safer in the case of breakage. Mercury vapours can have a lot of negative effects on the human body, some of them so bad that enough of it can be fatal. Mercury is also difficult to recycle properly and can therefore be tedious to dispose of.
Despite this, there is a slight issue with LEDs in regards to their materials used that should be addressed. Most of the materials used are different plastics and silicone, which for the most part are easy to recycle and not very harmful to do so. There is however one ingredient to them that is slightly problematic, and this material is phosphor.
Phosphor by itself is not dangerous to humans, the problem with phosphor is that it is a non-renewable material that is on its way to possibly running out.
Today phosphor is mostly used as a fertilizer material within the cultivation industry. While the amount of phosphor used here is estimated to decrease over time, it would cause it to run out within the next 50-100 years at today’s rate of consumption.
This is rather hard to calculate however and may not be extremely accurate since different sources claim widely different things, but the general consensus is that the phosphor supply is declining. The urgency of the situation is therefore unclear and should be monitored for further revelations.
Conclusion
LED lighting is an excellent lighting solution for a vast majority of situations, whether that is in usage at home, commercially or decorative lighting. However, there might be very specific situations in which some other form of lighting might serve the intended purpose better, but more often than not you won’t go wrong with an LED light.
That being said, there are a fair amount of negatives about LED lighting that should be taken into consideration. You can read our article on the disadvantages of LED lighting here.



