How LED Light Strips Work
LED strips are a flexible lighting solution that is mainly used for accent lighting, backlighting, or other decorative applications in a similar fashion. They are often used this way due to their physical ability to be slotted in wherever they are needed as they can be adjusted for length and other properties depending on their destined application.
Here we will cover how these LED strips work on a technical level as well as how they are powered and function on a practical scale.
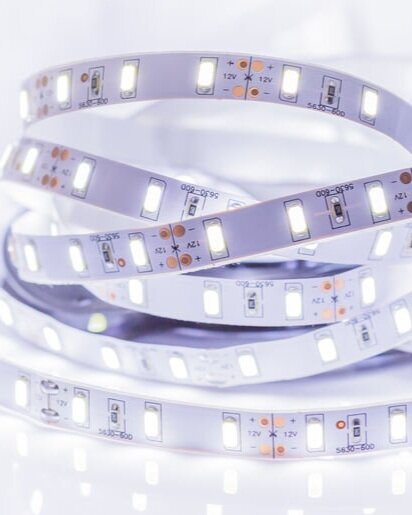

The Anatomy Of LED Strips
The anatomy of an LED strip is actually relatively simple. The LED strip consists of the main circuit board which has several identical LEDs chips mounted on it along its length. These singular LEDs are all connected via this circuit board, which allows them to function in unison.
However, all of the singular LEDs are connected parallel to each other, meaning that they are in no way dependent on each other in order to function. This means that it’s possible to cut the strip at any length without it disturbing the desired original strip. It is advised though to cut it along the premarked lines that are visible on top of the strip.
It is also standardized for LED strips to have some sort of adhesive on the back of them which allows for easy installation/mounting wherever is deemed fitting.
How LED Strips Function
LED strips function with a DC current that goes through the entire circuit board and through the LEDs mounted on it. In order to get a DC current from the available AC current commonly found in home outlets, it is usually required to use an LED driver.
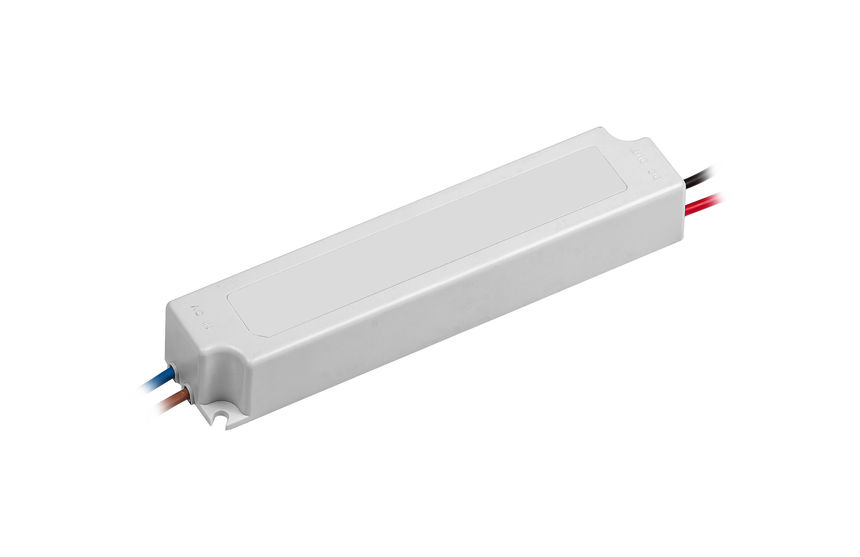
As said, these components simply transform the regular AC current into a more manageable DC current, which is what LEDs require in order to function. Theoretically, it is possible for LEDs to function on AC current as well but it is simply not practical to do so on a smaller scale such as LED strips.
The DC current from the driver is then connected to one of the ends of the strip in order to power it. Traditionally in DC wiring, there will be a red and a black cable coming out of the driver which should then be connected to the strip. The strip should have a + (positive) sign and a – (negative) sign next to a small copper area in which you solder the copper cables. In this case, you connect red to positive and black to negative. Otherwise, the strip is already connected to the driver and this step becomes obsolete.
These LED drivers are also usually where the controlling functions reside. This means that there are usually extra inputs on the driver, which allows for external signals from a light switch, dimmer switch, or any other switch function which controls it. This allows you to control the light intensity relatively simply and even other functions such as color or light temperature if the LED and the driver are built for it.

How Coloured RGB LED Strips Function

Coloured LED strips work in a similar fashion to how regular strips work, they are simply a bit more complex in how they are constructed. Instead of the regular white LED chips present in regular white strips, there is instead a mix of colored ones. The colors used instead are red, green, and blue (RGB) because when mixing these 3 colors you can create any color of light you desire. This is however if you want a strip that can change between different colors, if what you seek is a strip that only emits one specific color there are strips designed for this specific purpose instead.
If you have a strip of a singular color they work in a similar fashion as the regular strips due to their construction being virtually the same excluding the colored LED chips used in the color version. However, with the RGB version, it requires a bit more light control in order to get it working properly.
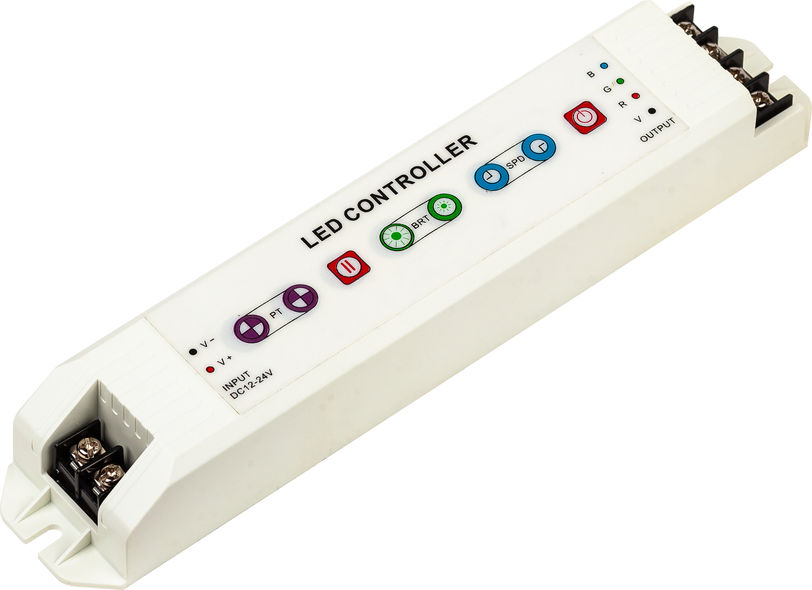

For RGB strips it is needed to have a driver which is capable of controlling both the light intensity of the strip but also which color should be emitted. This is done with extra inputs and outputs through the driver. The extra input slots are used for commanding which color you wish to be emitted and the extra output slots will give power to the different colors in different amounts depending on what color is desired. This is how the process of mixing colors is possible.
The RGB strips work great for creating different colors on the strip, however, there is one color they are not good at creating, which is white. White light is created when you combine an equal amount of red, green, and blue light in an RGB strip, however, the white light becomes uneven and slightly muddy in an application such as LED strips. This is why for applications that require a specific white light it is often better to use an RGBW strip.

RGBW LED Strips
Simply put, RGBW LED strips are a combination of regular LED strips and RGB strips. These strips have all the capabilities of an RGB strip but with the addition of ordinary white LED chips. These white LED chips’ main function is to simply supply a clean source of white light, which improves the overall quality of the mixed light this strip can create.
This does however mean that you will need a driver which is compatible with this extra white unit as well, but assuming that is present the RGBW strip is simply an upgrade in terms of light quality. Despite this, they can be a bit overkill depending on the application it is being used for, but if the quality of light is the main priority then RGBW strips should definitively be considered as they are a great option.